- The Government of Indonesia has made and issued several regulations regarding the carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia, one of which is law number 4 of 2023 concerning the Development and Strengthening of the Financial Sector (P2SK Law).
- The mechanism of the government’s role with companies in the carbon industry has several stages; Determination of Emission Limits, Distribution of Emission Permits, Trading of Permits and Monitoring and Verification.
- The carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia has several challenges faced by companies and the government as the main actors: Effective Carbon Pricing, Market Abuse or Manipulation, Unequal Access to Resources and Limited Supervision and Law Enforcement.
Indonesian Government Regulations
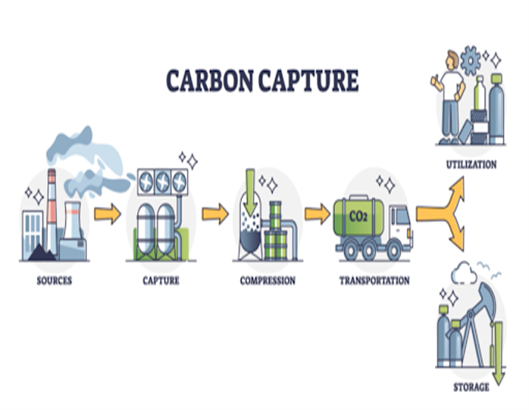
In line with Indonesia’s commitment to the Paris agreement initiated by the United Nations in 2015 coupled with technological and scientific advances regarding carbon capture technology. The carbon capture method began to be implemented in the industrial ecosystem and created a carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia. The government as a regulator has made and issued a law regarding carbon trading in Indonesia, Law number 4 of 2023 concerning the Development and Strengthening of the Financial Sector (P2SK Law) regulates carbon trading in Indonesia can be carried out through carbon exchanges. In addition, there are several other regulations regarding carbon trading in Indonesia:
- Law number 7 of 2021 concerning the Harmonization of Tax Regulations (HPP Law) which regulates carbon taxes.
- Law number 17 of 2004 concerning the Ratification of the Kyoto Protocol which affirms Indonesia’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regulation of the Minister of Environment and Forestry Number 21 of 2022 concerning the Implementation of Carbon Economic Values.
Through the Financial Services Authority (OJK), it is tasked with supervising carbon exchange operators, market infrastructure, service users and the settlement of carbon unit transactions in the carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia.
Read Also:
- Limbah Elektronik: Pengolahan Secara Berkelanjutan
- 5 Strategi Efektif Negara di Dunia dalam Mengatasi Banjir
How does the Carbon Industry Ecosystem in Indonesia work?

Companies and government agencies are the main players in the carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia; The company plays the role of a party that conducts carbon trading. Meanwhile, the government performs its function as a facilitator and regulator in the carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia. The mechanism of the government’s role with companies in the carbon industry has several stages:
- Determination of Emission Limits (CAP): The government or authority sets emission limits.
- Distribution of Emission Permits: Companies receive emission permits based on predetermined limits.
- Permit trading: Companies that successfully reduce emissions can sell unused permits in the carbon market to other companies.
- Monitoring and Verification: Each company must report their emissions, which are then verified by a third party to ensure the validity of the data.
Read Also:
- Perusahaan Eksplorasi Menjaga Keberlanjutan Lingkungan dalam Sektor CCS
- Pemanfaatan Limbah Kotoran sebagai Sumber Energi dan Pupuk Organik
The Future of the Carbon Industry in Indonesia

Indonesia has committed to achieving the carbon emission reduction target set by the NDC of 31.89% by 2030. The carbon exchange and carbon exchange mechanism in Indonesia were opened on September 26, 2023. There are 50 companies that have obtained carbon exchange permits with a total volume of 501,910 tons of CO2 equivalent until the period of February 29, 2024. There are three phases of carbon trading in Indonesia:
- Phase 1 will be carried out in the period (2023-2024), with a focus on coal power plants connected to the PLN network only.
- Phase 2 is planned to be implemented in the period (2025-2027), with plans to expand the scheme to include coal-fired power plants with a capacity of less than 25 MW, gas-fired power plants, combined-cycle power plants, and other coal-fired power plants that are not connected to the PLN grid.
- Phase 3 will be implemented in the period (2028-2030), covering all fossil fuel power plants, including diesel power plants with a capacity of 2 MW or more.
The carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia has several challenges faced by companies and the government as the main actors:
- Effective Carbon Pricing: One of the main challenges in the carbon trading system is determining the right carbon price.
- Market Abuse or Manipulation: Companies could cheat on emissions reduction data or buy and sell carbon permits in a way that harms the market.
- Unequal Access to Resources: There is an inequality in access to technology and human resources in certain countries or companies to be involved in the carbon industry ecosystem in Indonesia.
- Limitations of Supervision and Law Enforcement: Some government agencies have weak regulations or are unable to effectively monitor the carbon market.
#zonaebt #sebarterbarukan #ebtheroes
Editor: Tri Indah Lestari