
- Indonesia has a red list index value of 0.75 which indicates a low extinction value
- Indonesia’s red list index value has decreased since 2000 or there has been an extinction of biodiversity in Indonesia
- The government continues to make efforts through conservation efforts with an increasing area of conservation areas
- The main problem of extinction is poaching and illegal trade
Read More
- Dilema Penggunaan Tote Bag, Sebuah Solusi atau Masalah Baru?
- How to Achieve 10% Marine Protected Areas in Indonesia
The tropics are home to more than half of the world’s biodiversity. Indonesia as one of the tropical countries in the world has a lot of biodiversity even though it only has an area of 1.3% of the total area of the earth. The total amount of biodiversity in Indonesia ranks second after Brazil, first rank in the ocean and second rank on land.
Biodiversity is a world issue and is included in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Biodiversity in the ocean is regulated in SDG 14 on life below water and on land and inland waters is regulated in SDG 15 on life on land. This article focuses on terrestrial animals and the red index list of species survival.
What is the Red List Index of Species Survival?
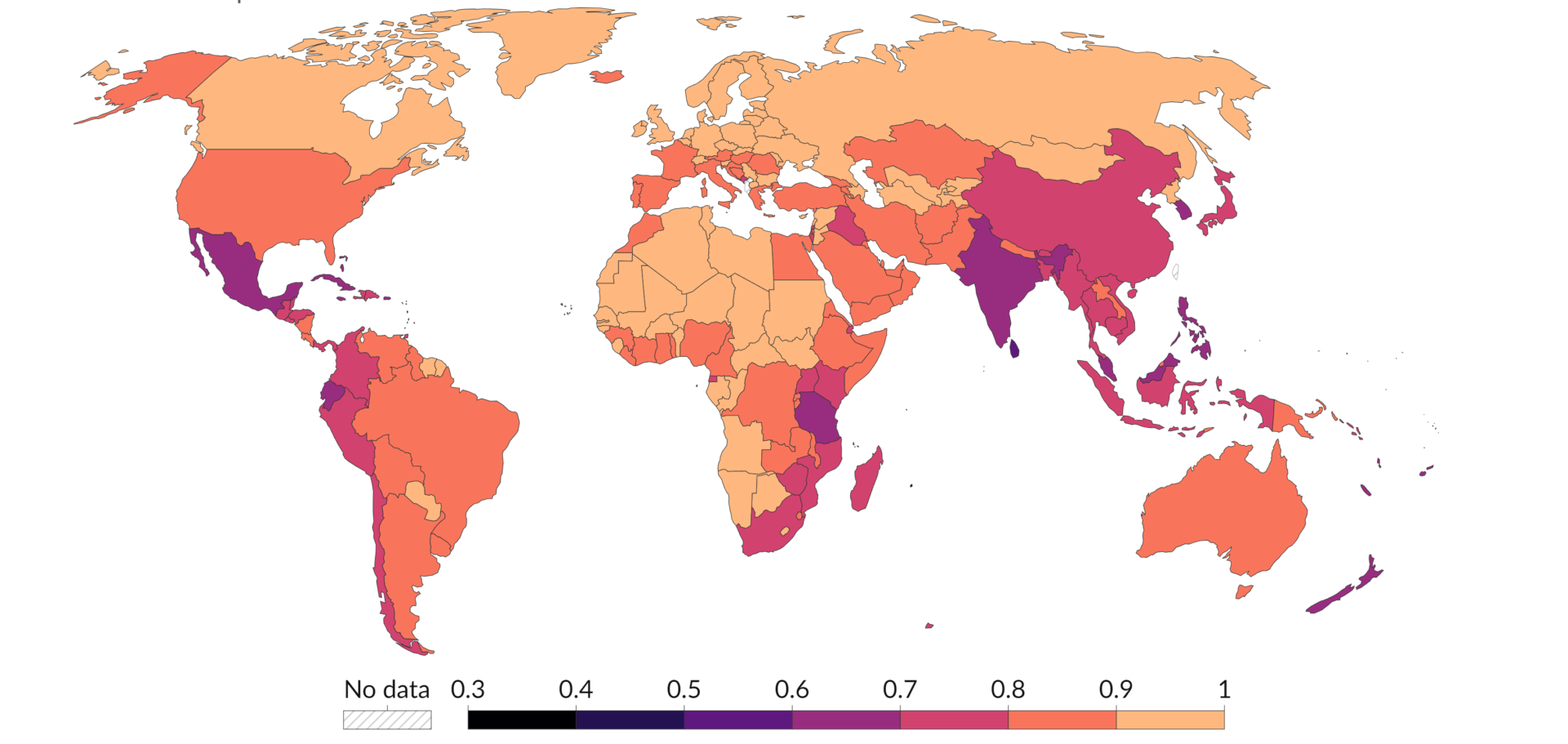
The red list index (RLI) is a number that describes the threat of biodiversity extinction through changes in threat status and species loss. The calculation of the red list index is based on data from the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The analyzed in this index is in the form of taxa of amphibians, mammals, aves, and reptiles.
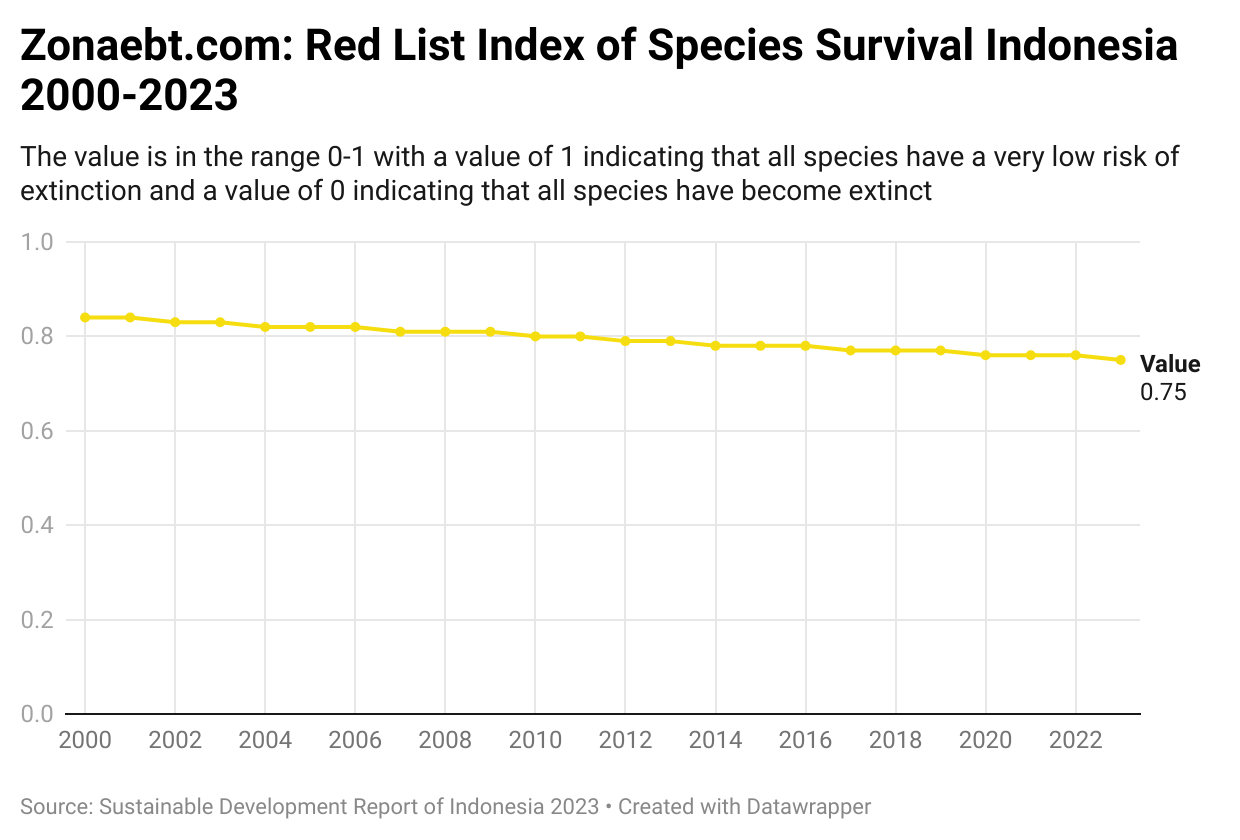
The red list index value has a range of 0-1 with a value of 0 indicating extinct status or all species have become extinct and a value of 1 indicating the status of least concern or very low risk of extinction. In fact, Indonesia obtained a value of 0.75 which means it has a low species extinction value. However, Indonesia experienced a decrease in the index value which shows the increasing extinction of biodiversity, especially animals in amphibian taxa, mammals, aves, and reptiles.
What is the Actual Condition of Biodiversity in Indonesia?

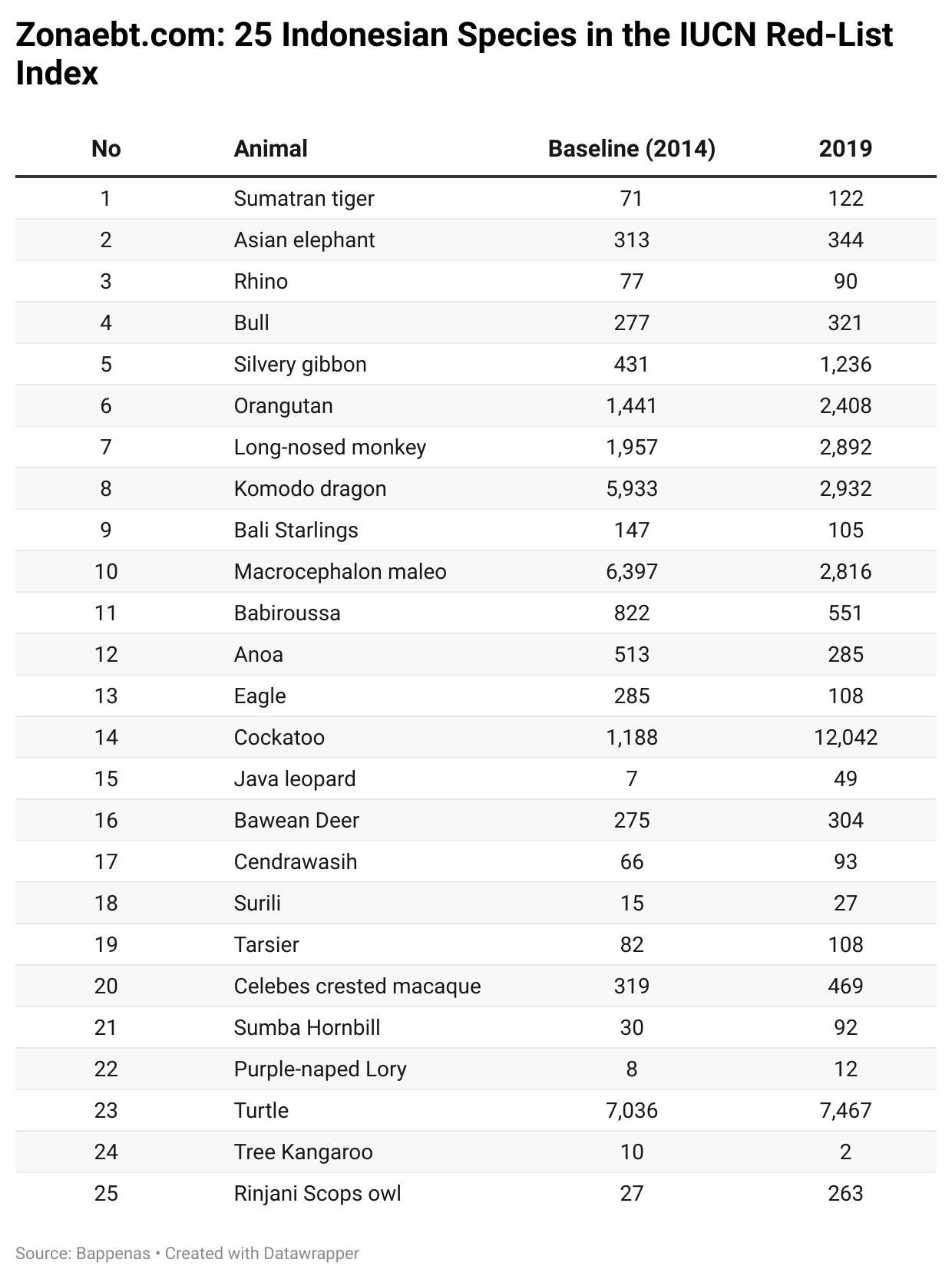
Data on biodiversity by the Ministry of Environment and Forestry shows declining results. However, there has been a significant increase in animal populations such as proboscis monkeys, gibbons, and orangutans with each increasing by around 1000 individuals in the 2014-2019 period. Some species such as parrots have increased by more than 10 thousand heads from 1188 in 2014 to 12 thousand heads in 2019. Data on Indonesia’s priority species changes by the Ministry of Environment and Forestry in 2014 and 2019 are as follows.
Extinct species of animals experience a lot of poaching and illegal trade. During 2015-2022 there was an increase and decrease in cases of illegal plants and animals through poaching and illegal trade. Plant and wildlife cases in 2015 found 43 cases and there was a decrease to 35 cases in 2022. However, in 2019 there was an increase in cases to reach 65 cases. The problem of poaching and illegal trade is still a problem because it can increase the extinction rate of Indonesia’s rare animals and plants.
What is the Government doing in response to the issue of Biodiversity?

The Ministry of Environment and Forestry prepared the National Red List Index (RLI) based on global assessments. The list contains an assessment of 904 species from animalia and also plantae. The results of the analysis are expected to be an illustration of the success rate of various conservation efforts that have been carried out. In addition, the results of the national index red list analysis will also be used to determine the next steps in overcoming biodiversity problems.
Indonesia continues to make efforts to conserve biodiversity by expanding conservation areas. Indonesia has 25.94% of biodiversity conservation areas in 2022. This percentage has not increased since 2018 so Indonesia has a stagnant trend of conservation area growth. The figures show that the challenge regarding biodiversity in Indonesia is still a major problem.
Challenges and Solutions of Biodiversity Problem

Then, why is extinction still a problem in Indonesia? One of the main problems of biodiversity is the poaching of protected animals. In addition, changes in vegetation in an animal ecosystem are also one of the big challenges. Then, what are the efforts made by the government in dealing with these problems? The government has made various efforts as follows:
- Affirmative forest and silviculture protection for increased biodiversity and use value of conservation areas
- Conservation areas
- Management of biodiversity corridors for important species
- Protection of biodiversity and germplasm sources
The government also conducts law enforcement against poaching or illegal trade in plants and wildlife. In addition, the government also secures and restores forest areas and the circulation of forest products. Law enforcement is an effort to prevent biodiversity extinction and provide economic, social, and ecological benefits. Law enforcement is also carried out to support the achievement of prosperity and welfare of the community.
Read More
- Circular City is Possible: Berkumpulnya Startup Ekonomi Sirkular di Surabaya Waste Up Project 2023
- Simak 5 Komunitas Peduli Lingkungan, Apakah Kamu Ikut Serta di Dalamnya?
In conclusion, biodiversity extinction in Indonesia is still a problem even though Indonesia has a fairly high red list index value. The government has made various efforts to overcome the problem of extinction, but it needs the role of the community in supporting and enforcing government policies. So, what have you done to avoid biodiversity extinction?
#ZonaEBT #sebarterbarukan #EBTHeroes
Editor: Bellinda Putri Hidayat






Comment closed