- Carbon trading is a mechanism for determining the economic value of carbon by adopting a market mechanism between countries or companies in the world.
- Carbon trading activities in the world have been regulated by the UNCC (United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change) tasked with supervising carbon quotas and credits for each country in the world. There are three types of carbon trading mechanisms; Clean Development Mechanism, Joint Implementation, and Cap & Trade.
- Indonesia has two main opportunities in carbon trading. First, nature-based by utilizing nature such as forests, mangroves, peatlands or dry forests. The second is technology-based as a greenhouse gas emission reduction mitigation project.
What is Carbon Trading?

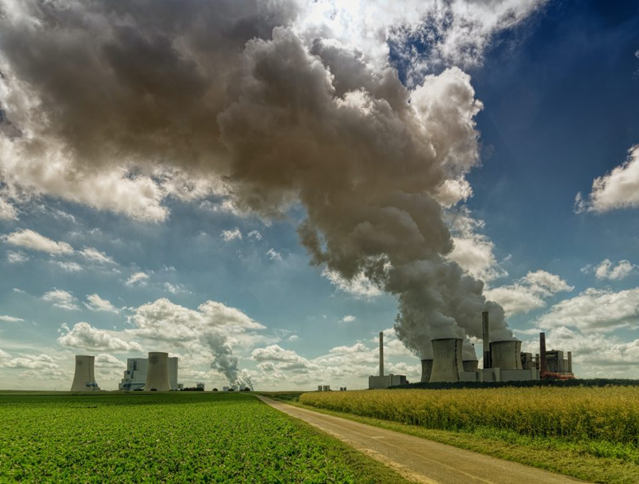
Along with the impact of the climate crisis felt by living things on earth, it has increased and endangered life on earth. The main cause of the climate crisis is carbon emissions produced by human activities for many years. In response, countries around the world have made a commitment called Net Zero Emission (NZE) 2060, which is the goal to reduce carbon emissions on earth. One of the government’s concrete steps in achieving the Net Zero Emission 2060 goal is to trade carbon.
Carbon trading is a mechanism for determining the economic value of carbon by adopting a market mechanism between countries or companies in the world. Carbon trading operates with a quota and credit system, usually in the form of carbon emission certificates produced, countries or companies that succeed in reducing carbon emissions with predetermined standards can sell their carbon credit certificates to countries or companies that need more carbon emission quotas. Carbon trading activities in the world have been regulated in the 2015 Paris agreement.
Baca Juga
How is the mechanism of carbon trading?
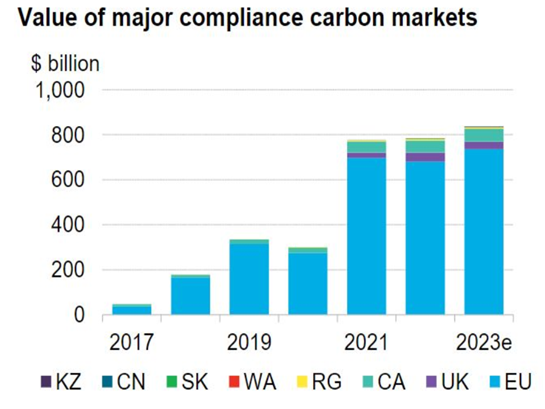
Carbon trading activities in the world have been regulated by the UNCC (United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change) tasked with supervising carbon quotas and credits for each country in the world to achieve Net Zero Emission 2060. The UNCC offers three types of carbon trading mechanisms.
- Clean Development Mechanism (CDM)
CDM is a form of cooperation or collaboration between developing countries and developed countries to achieve Net Zero Emission. Article 12 of the Kyoto Protocol states that the purpose of the CDM is:
- Assisting developed countries classified as Annex I countries to meet their country’s emission reduction targets.
- Assist developing countries that are not included in Annex I to implement sustainable development and contribute to the achievement of the main goal of the climate change convention, which is to reduce the concentration of world greenhouse gas emissions in order to prevent the occurrence of the earth’s climate crisis.
- Joint Implementation (JI)
JI is generally used in developed countries (Annex I) and industrial countries (Annex B) by collaborating in the field of investment or technology cooperation that is more environmentally friendly for the industrial sector.
- Emission Trading (Cap & Trade)
The Cap & Trade mechanism is carried out by business actors or industrial companies that exceed the carbon emission quota limit that has been set. Each company has an emission quota limit that has been set in the Emission Upper Limit Technical Approval. Companies will be allocated emission quotas. Companies are required to report the achievement of their emission quotas at the end of the predetermined period.
Baca Juga
How Indonesia’s Carbon Trading Potential?
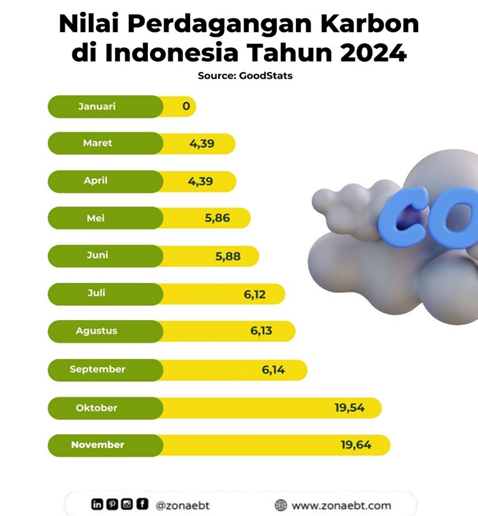
Indonesia already has several regulations regarding the Carbon trading mechanism that has been established. Some examples of carbon trading regulations in Indonesia are Government Regulation Number 98 of 2021, Law Number 7 of 2021 and Presidential Decree Number 13 of 2023. Regulations have been made by the government not only regulating carbon trading but also to achieve Indonesia’s target of Net Zero Emission.
According to the Carbon Trade Association, Indonesia has two main opportunities in carbon trading. The First is nature-based by utilizing nature such as forests, mangroves, peatlands or dry forests. The second is technology-based as a greenhouse gas emission reduction mitigation project in accordance with the criteria set by the Indonesia Carbon Exchange. Both opportunities can significantly reduce carbon emissions and create an industry based on environmentally friendly technology. Carbon trading has many benefits for society and the planet:
- Supporting public policy objectives
- Improving air quality
- Supporting low-carbon innovation and technology
- Opening up new economies for developing countries
- Monitor the amount of emissions produced by a country
#zonaebt #EBTHeroes #serbaterbarukan
Editor: Tri Indah Lestari