
- Biodiesel is a type of alternative fuel that is produced through a chemical reaction between vegetable oil or animal fat with alcohol (ethanol or methanol) with the help of catalysts, which are commonly used such as sodium potassium hydroxide.
- Biodiesel and Diesel are the types of fuels used in diesel engines, but they have some differences in their management sources, emissions, sulfur content, and oxidation reactions.
- Although the use of biodiesel in Indonesia continues to increase from year to year, in addition to the advantages of biodiesel when compared to fossil fuels, biodiesel also has shortcomings and is still undergoing a development process.
What is Biodiesel?
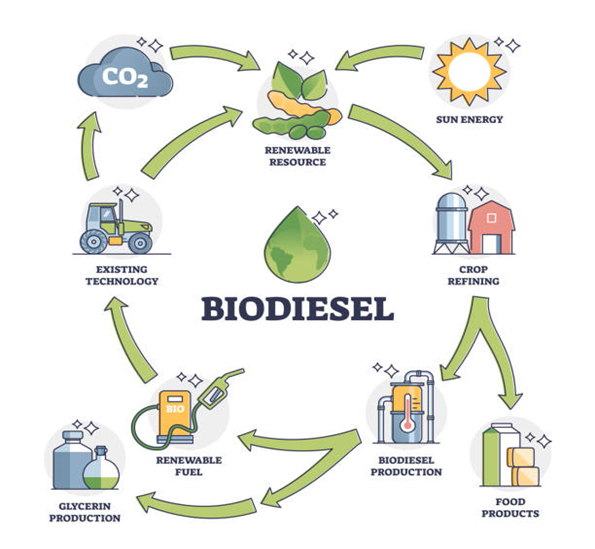
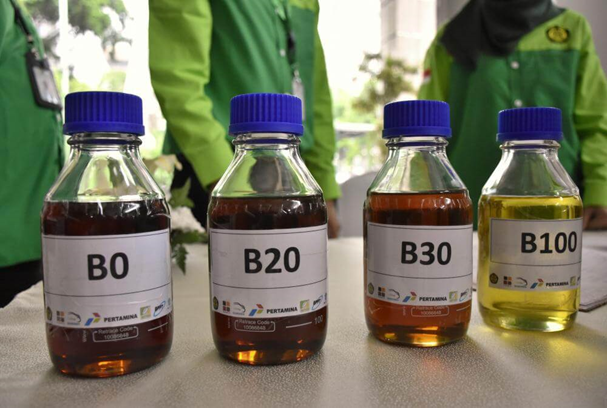
Biodiesel is one of the alternative sources of renewable fuel to replace diesel fuel derived from petroleum. Biodiesel is a type of alternative fuel that is produced through a chemical reaction between vegetable oil or animal fat with alcohol (ethanol or methanol) with the help of catalysts. Commonly used catalysts include sodium potassium hydroxide. Biodiesel comes from various types of organic matter, plant or animal that are natural in origin, such as crude palm oil, soybean oil, castor oil, Calophyllum inophyllum oil, fish oil, and palm fatty acid distillate (PFAD). Biodiesel has several types based on the composition of its mixture, such as:
- B20 biodiesel is the result of mixing 20% biodiesel with 80% diesel fuel oil.
- B30 & B35 biodiesel is the result of blending 30% biodiesel with 70% diesel fuel oil.
- Biodiesel B100 is a fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) made from vegetable oils or animal fats through an esterification or transesterification process.
Biodiesel is currently widely used in various sectors such as micro enterprises, agriculture, fisheries, transportation, power plants, industry and commercial.
Baca Juga
- Peralihan Energi dengan Penanaman Pohon Biomassa di Indonesia
- Mobil Listrik: Hemat atau Sekedar Tren Sesaat
Difference Between Biodiesel and Diesel
Biodiesel and Diesel are the types of fuel used in diesel engines, but they have some differences in their management source, emissions, sulfur content, and oxidation reactions.
- Fuel Source
Biodiesel is produced through a chemical reaction between vegetable oils or animal fats with alcohol (ethanol or methanol) with the help of catalysts, which are commonly used such as; sodium potassium hydroxide. Biodiesel comes from various types of organic matter, plant or animal that are natural in nature, such as crude palm oil, soybean oil, castor oil, Calophyllum inophyllum oil, fish oil, and palm fatty acid distillate (PFAD). Meanwhile, diesel comes from the crude petroleum refining process, where fractions are separated through distillation process to produces a mixture of carbon chains containing between 9-25 carbon atoms per molecular.
- Emission
Biodiesel can produce emissions in the production process and transportation use, but in general, biodiesel produces lower emissions than fossil fuels in this case diesel. According to research from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the use of biodiesel can reduce emissions by 50-86% compared to diesel fuel. In other words, diesel produces much greater carbon dioxide emissions compared to biodiesel.
- Sulfur Content
The sulfur content derived from the diesel combustion reaction in the engine can form a colorless gaseous compound called sulfur dioxide. Based on research by the Engineering Study Program at the Shipbuilding Institute of Polytechnic Surabaya (SHIPS), states that the main component of diesel, namely hydrocarbon compounds, produces higher sulfur dioxide emissions, while biodiesel can reduce sulfur dioxide emissions by 100%.
- Oxidation Reaction
The combustion reaction between diesel in the engine produces carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbon emissions, whereas the emissions from the combustion reaction between biodiesel in the engine are lower and cleaner.
Baca Juga
Sumber Daya Biomassa, Bisa Didapat dari Mana Saja?
Biofuel Energi Masa Depan Indonesia yang Dipertimbangkan
Advantages and Disadvantages of Biodiesel
Although the use of biodiesel in Indonesia continues to increase from year to year, in addition to the advantages of biodiesel compared to fossil fuels, biodiesel also has shortcomings and is still undergoing development.
Advantages
- Less emissions
Both production and combustion of Biodiesel often release up to 90% less CO2 than regular diesel.
- Low maintenance and safety
Biodiesel contain FAME (Fatty Acid Methyl Ester) from animals or plants product so that the filter in the tank is cleaner and not contaminated with harmful substances. Biodiesel also has a lower freezing point than diesel, making it suitable for use in cold weather conditions.
- Odorless
Biodiesel derived from organic sources of vegetable and animal fats, emits fewer pollutants and is cleaner so it tends to be more environmentally friendly both for the environment and humans.
- Same performance as diesel
Biodiesel can be applied to engines with various functions without requiring modifications. In fact, the engine performance is almost the same as diesel fuel.
Disadvantages
- Raw Material Limitations
Biodiesel comes from the extraction of plant and animal products sourced from the agricultural and livestock sectors, so it requires land use that can contribute to land clearing by deforestation. Besides that, the availability of suitable plant and animal species is limited.
- Large Investment Costs
The production process, raw materials, and the distribution of biodiesel requires greater investment compared to diesel fuel.
#zonaebt #EBTHeroes #Sebarterbarukan
Editor: Tri Indah Lestari
Referensi
- Pengertian Biodiesel
- Pengertian Biodiesel: Jenis, Manfaat dan Contoh
- Apa itu Biosolar, Bahan Pembuatan, Kelebihan, dan Perbedaannya dengan Solar
- Perbandingan Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca antara Pembakaran Solar dan Biodiesel
- Irfan Saiful, Purnomo Hendra. 2018. Studi Komparasi Emisi Gas Buang Mesin Diesel Menggunakan Bahan Bakar Solar dan Minyak Kelapa (Virgin Coconut Oil) Vol. 3 No 1: 18-25
- Kelebihan dan Kekurangan Biodiesel HVO




